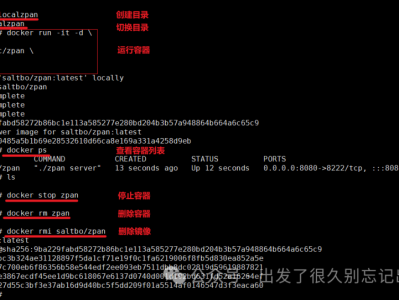
# Harbor服务器假设主机ip为192.168.186.128,HTTP端口为8080,HTTPS端口为8443# 测试机器主机ip:只要可以访问Harbor主机即可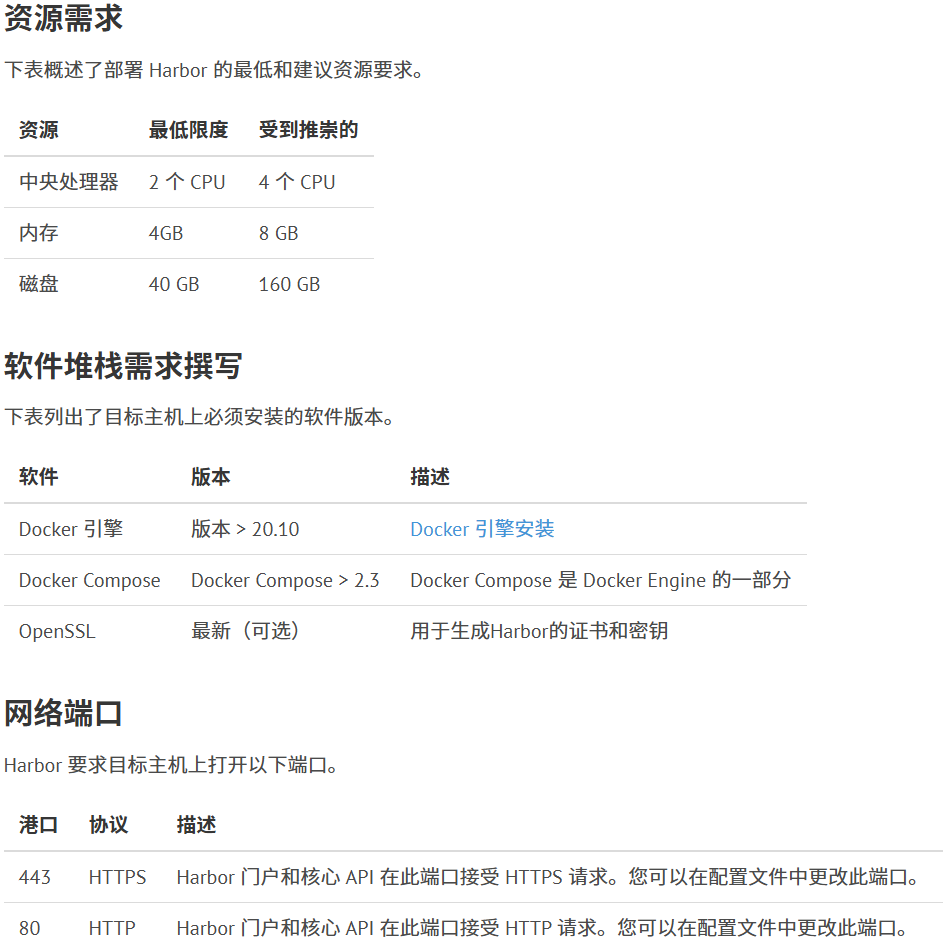
# 详见:https://goharbor.io/docs/2.13.0/install-config/run-installer-script/#connect-http说明:需要准备两台机器,如果只是做测试,可以使用虚拟机模拟这种环境一台机器给harbor使用,同时harbor未开启https配置,即在harbor.yml注释https配置另一台机器做测试,使用http访问,推送镜像到harbor,需要做如下配置如果想在harbor机器上测试docker login,也需要做如下操作{ "registry-mirrors": [ "https://docker.m.daocloud.io" ], "insecure-registries": ["ip:端口 或者 域名:端口,如192.168.186.128:8080"]}systemctl restart docker
# 详见:https://goharbor.io/docs/2.13.0/install-config/configure-https/以下步骤假设您的 Harbor 注册表的主机名是yourdomain.com,并且其 DNS 记录指向您正在运行 Harbor 的主机。因为不使用域名,所以这里的yourdomain.com就是当前harbor机器的IP以下操作在harbor机器上操作openssl genrsa -out ca.key 4096
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -sha512 -days 3650 \ -subj "/C=CN/ST=Beijing/L=Beijing/O=example/OU=Personal/CN=MyPersonal Root CA" \ -key ca.key \ -out ca.crt
# 详见:https://goharbor.io/docs/2.13.0/install-config/customize-token-service/# 参数说明C=CN,国家ST=Beijing,省份/州L=Beijing,城市/地区O=example,组织/公司OU=Personal,其他内容CN=MyPersonal Root CA,域名/IPopenssl genrsa -out yourdomain.com.key 4096
# 调整选项中的值-subj以反映您的组织。如果您使用 FQDN 连接 Harbor 主机,# 则必须将其指定为通用名称 ( CN) 属性,并在密钥和 CSR 文件名中使用它。openssl req -sha512 -new \ -subj "/C=CN/ST=Beijing/L=Beijing/O=example/OU=Personal/CN=yourdomain.com" \ -key yourdomain.com.key \ -out yourdomain.com.csr# 说明:此处的yourdomain.com替换为harbor机器的IP,如192.168.186.128# 修改后的内容为:openssl req -sha512 -new \ -subj "/C=CN/ST=Beijing/L=Beijing/O=example/OU=Personal/CN=192.168.186.128" \ -key yourdomain.com.key \ -out yourdomain.com.csr# 无论您使用 FQDN 还是 IP 地址连接到 Harbor 主机,都必须创建此文件,# 以便为 Harbor 主机生成符合主体备用名称 (SAN) 和 x509 v3 扩展要求的证书。# 请将条目替换为DNS您的域名。cat > v3.ext <<-EOFauthorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuerbasicConstraints=CA:FALSEkeyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEnciphermentextendedKeyUsage = serverAuthsubjectAltName = @alt_names[alt_names]DNS.1=yourdomain.comDNS.2=yourdomainDNS.3=hostnameEOF# 说明:# 修改v3.ext文件中的[alt_names]到EOF这部分内容,如下所示:[alt_names]IP.1 = 192.168.186.128EOF# v3.ext文件内容:authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuerbasicConstraints=CA:FALSEkeyUsage = digitalSignature, nonRepudiation, keyEncipherment, dataEnciphermentextendedKeyUsage = serverAuthsubjectAltName = @alt_names[alt_names]IP.1 = 192.168.186.128# yourdomain.com将CSR和CRT文件名中的替换为Harbor主机名openssl x509 -req -sha512 -days 3650 \ -extfile v3.ext \ -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAcreateserial \ -in yourdomain.com.csr \ -out yourdomain.com.crt生成ca.crt、yourdomain.com.crt和yourdomain.com.key文件后,将它们提供给Harbor和Docker,并重新配置Harbor以使用它们。
mkdir -p /data/cert/\cp yourdomain.com.crt /data/cert/\cp yourdomain.com.key /data/cert/# 说明:# harbor.yml文件,修改内容如下:......https: port: 【修改端口,8443】 certificate: 【指定证书,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.crt】 private_key: 【指定密钥,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.key】......此处的/data/cert我harbor.yml文件中的https的certificate、private_key字段的值假设把证书、密钥放在/data/cert目录下# 创建目录命令:mkdir -p /data/cert/# 如果certificate的值为为/data/cert/yourdomain.com.crt执行命令:\cp yourdomain.com.crt /data/cert/# 如果private_key的值为/data/cert/yourdomain.com.key,执行命令:\cp yourdomain.com.key /data/cert/# Docker守护进程将.crt文件解释为CA证书,.cert将文件解释为客户端证书。openssl x509 -inform PEM -in yourdomain.com.crt -out yourdomain.com.cert
说明:在测试机器上需要执行以下操作如果想在harbor机器上测试docker login,也需要做如下操作
mkdir -p /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/\cp yourdomain.com.cert /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/\cp yourdomain.com.key /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/\cp ca.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com/# 如果将默认nginx端口443映射到其他端口,# 请创建文件夹# /etc/docker/certs.d/yourdomain.com:port、或# /etc/docker/certs.d/harbor_IP:port。# 说明:因为使用的是IP,HTTPS端口为8443,所以要创建目录/etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/# /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/目录有以下文件:yourdomain.com.certyourdomain.com.keyca.crt# 执行命令:mkdir -p /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/# 方式1:# 复制yourdomain.com.cert、yourdomain.com.key、ca.crt这三个文件\cp yourdomain.com.cert /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/\cp yourdomain.com.key /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/\cp ca.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/# 方式2:# 或者也可以复制yourdomain.com.crt# \cp yourdomain.com.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443/# 方式3:# 或者通过浏览器下载证书192.168.186.128.crt# \cp 192.168.186.128.crt /etc/docker/certs.d/192.168.186.128:8443//etc/docker/certs.d/ └── yourdomain.com:port ├── yourdomain.com.cert <-- Server certificate signed by CA ├── yourdomain.com.key <-- Server key signed by CA └── ca.crt <-- Certificate authority that signed the registry certificate
systemctl restart docker
# 修改配置文件harbor.yml文件启用https配置,修改ports、certificate、private_key等字段# harbor.yml文件,修改内容如下:......https: port: 【修改端口,8443】 certificate: 【指定证书,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.crt】 private_key: 【指定密钥,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.key】......# 执行脚本./prepare# 停止并销毁容器docker-compose down# 创建并启动容器docker-compose up -d浏览器访问,可能会显示警告,“您的连接不是私密连接”/etc/docker/daemon.json文件取消-insecure-registry配置# 登录harbor:docker login yourdomain.comdocker login yourdomain.com:port# 说明:# 使用8080端口登录:# docker login 192.168.186.128:8080# 使用8443端口登录:# docker login 192.168.186.128:8443如果尚未部署Harbor,请参阅“配置Harbor YML文件”以获取有关如何通过指定hostname和https属性来配置Harbor以使用证书的信息harbor.yml。如果已经使用HTTP部署了Harbor并想要将其重新配置为使用HTTPS,请执行以下步骤。# Harbor使用一个nginx实例作为所有服务的反向代理。# 可以使用prepare脚本配置nginx使用HTTPS。# 该脚本prepare位于Harbor安装程序包中,与install.sh脚本位于同一级别。./prepare
# 镜像数据保留在文件系统中,因此不会丢失任何数据。docker compose down -v
docker compose up -d
打开浏览器并输入https://yourdomain.com。它应该会显示 Harbor 界面。某些浏览器可能会显示警告,指出证书颁发机构 (CA) 未知。这是因为您使用的自签名 CA 并非来自受信任的第三方 CA。您可以将 CA 导入浏览器以消除此警告。在运行Docker守护程序的计算机上,检查/etc/docker/daemon.json文件以确保未为https://yourdomain.com -insecure-registry设置该选项。
# 从Docker客户端登录Harbor。docker login yourdomain.com# 如果您已将nginx的443端口映射到其他端口,请在login命令中添加该端口。docker login yourdomain.com:port详见:https://goharbor.io/docs/2.13.0/install-config/configure-internal-tls/
# 取消internal_tls、enable、dir前面的注释# harbor.yml文件,修改内容如下:https:...... internal_tls: enabled: true dir: 【tls目录,如/etc/harbor/tls/internal】......./prepare
# 命令:# docker run -v /:/hostfs goharbor/prepare:<current_harbor_version> gencert -p /path/to/internal/tls/cert# 示例:# 假设当前current_harbor_version的值为v2.13.0docker run -v /:/hostfs goharbor/prepare:v2.13.0 gencert -p /data/internal/tls/certwget https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v2.13.0/harbor-online-installer-v2.13.0.tgz
tar -xf harbor-online-installer-v2.13.0.tgz
harbor├── common.sh├── harbor.yml.tmpl├── install.sh├── LICENSE└── prepare0 directories, 5 filescd harbor
# Configuration file of Harbor# The IP address or hostname to access admin UI and registry service.# DO NOT use localhost or 127.0.0.1, because Harbor needs to be accessed by external clients.hostname: reg.mydomain.com# http related confighttp: # port for http, default is 80. If https enabled, this port will redirect to https port port: 80# https related confighttps: # https port for harbor, default is 443 port: 443 # The path of cert and key files for nginx certificate: /your/certificate/path private_key: /your/private/key/path # enable strong ssl ciphers (default: false) # strong_ssl_ciphers: false# # Harbor will set ipv4 enabled only by default if this block is not configured# # Otherwise, please uncomment this block to configure your own ip_family stacks# ip_family:# # ipv6Enabled set to true if ipv6 is enabled in docker network, currently it affected the nginx related component# ipv6:# enabled: false# # ipv4Enabled set to true by default, currently it affected the nginx related component# ipv4:# enabled: true# # Uncomment following will enable tls communication between all harbor components# internal_tls:# # set enabled to true means internal tls is enabled# enabled: true# # put your cert and key files on dir# dir: /etc/harbor/tls/internal# Uncomment external_url if you want to enable external proxy# And when it enabled the hostname will no longer used# external_url: https://reg.mydomain.com:8433# The initial password of Harbor admin# It only works in first time to install harbor# Remember Change the admin password from UI after launching Harbor.harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345# Harbor DB configurationdatabase: # The password for the user('postgres' by default) of Harbor DB. Change this before any production use. password: root123 # The maximum number of connections in the idle connection pool. If it <=0, no idle connections are retained. max_idle_conns: 100 # The maximum number of open connections to the database. If it <= 0, then there is no limit on the number of open connections. # Note: the default number of connections is 1024 for postgres of harbor. max_open_conns: 900 # The maximum amount of time a connection may be reused. Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse. If it <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's age. # The value is a duration string. A duration string is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as "300ms", "-1.5h" or "2h45m". Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h". conn_max_lifetime: 5m # The maximum amount of time a connection may be idle. Expired connections may be closed lazily before reuse. If it <= 0, connections are not closed due to a connection's idle time. # The value is a duration string. A duration string is a possibly signed sequence of decimal numbers, each with optional fraction and a unit suffix, such as "300ms", "-1.5h" or "2h45m". Valid time units are "ns", "us" (or "µs"), "ms", "s", "m", "h". conn_max_idle_time: 0# The default data volumedata_volume: /data# Harbor Storage settings by default is using /data dir on local filesystem# Uncomment storage_service setting If you want to using external storage# storage_service:# # ca_bundle is the path to the custom root ca certificate, which will be injected into the truststore# # of registry's containers. This is usually needed when the user hosts a internal storage with self signed certificate.# ca_bundle:# # storage backend, default is filesystem, options include filesystem, azure, gcs, s3, swift and oss# # for more info about this configuration please refer https://distribution.github.io/distribution/about/configuration/# # and https://distribution.github.io/distribution/storage-drivers/# filesystem:# maxthreads: 100# # set disable to true when you want to disable registry redirect# redirect:# disable: false# Trivy configuration## Trivy DB contains vulnerability information from NVD, Red Hat, and many other upstream vulnerability databases.# It is downloaded by Trivy from the GitHub release page https://github.com/aquasecurity/trivy-db/releases and cached# in the local file system. In addition, the database contains the update timestamp so Trivy can detect whether it# should download a newer version from the Internet or use the cached one. Currently, the database is updated every# 12 hours and published as a new release to GitHub.trivy: # ignoreUnfixed The flag to display only fixed vulnerabilities ignore_unfixed: false # skipUpdate The flag to enable or disable Trivy DB downloads from GitHub # # You might want to enable this flag in test or CI/CD environments to avoid GitHub rate limiting issues. # If the flag is enabled you have to download the `trivy-offline.tar.gz` archive manually, extract `trivy.db` and # `metadata.json` files and mount them in the `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/db` path. skip_update: false # # skipJavaDBUpdate If the flag is enabled you have to manually download the `trivy-java.db` file and mount it in the # `/home/scanner/.cache/trivy/java-db/trivy-java.db` path skip_java_db_update: false # # The offline_scan option prevents Trivy from sending API requests to identify dependencies. # Scanning JAR files and pom.xml may require Internet access for better detection, but this option tries to avoid it. # For example, the offline mode will not try to resolve transitive dependencies in pom.xml when the dependency doesn't # exist in the local repositories. It means a number of detected vulnerabilities might be fewer in offline mode. # It would work if all the dependencies are in local. # This option doesn't affect DB download. You need to specify "skip-update" as well as "offline-scan" in an air-gapped environment. offline_scan: false # # Comma-separated list of what security issues to detect. Possible values are `vuln`, `config` and `secret`. Defaults to `vuln`. security_check: vuln # # insecure The flag to skip verifying registry certificate insecure: false # # timeout The duration to wait for scan completion. # There is upper bound of 30 minutes defined in scan job. So if this `timeout` is larger than 30m0s, it will also timeout at 30m0s. timeout: 5m0s # # github_token The GitHub access token to download Trivy DB # # Anonymous downloads from GitHub are subject to the limit of 60 requests per hour. Normally such rate limit is enough # for production operations. If, for any reason, it's not enough, you could increase the rate limit to 5000 # requests per hour by specifying the GitHub access token. For more details on GitHub rate limiting please consult # https://docs.github.com/rest/overview/resources-in-the-rest-api#rate-limiting # # You can create a GitHub token by following the instructions in # https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/creating-a-personal-access-token-for-the-command-line # # github_token: xxxjobservice: # Maximum number of job workers in job service max_job_workers: 10 # Maximum hours of task duration in job service, default 24 max_job_duration_hours: 24 # The jobLoggers backend name, only support "STD_OUTPUT", "FILE" and/or "DB" job_loggers: - STD_OUTPUT - FILE # - DB # The jobLogger sweeper duration (ignored if `jobLogger` is `stdout`) logger_sweeper_duration: 1 #daysnotification: # Maximum retry count for webhook job webhook_job_max_retry: 3 # HTTP client timeout for webhook job webhook_job_http_client_timeout: 3 #seconds# Log configurationslog: # options are debug, info, warning, error, fatal level: info # configs for logs in local storage local: # Log files are rotated log_rotate_count times before being removed. If count is 0, old versions are removed rather than rotated. rotate_count: 50 # Log files are rotated only if they grow bigger than log_rotate_size bytes. If size is followed by k, the size is assumed to be in kilobytes. # If the M is used, the size is in megabytes, and if G is used, the size is in gigabytes. So size 100, size 100k, size 100M and size 100G # are all valid. rotate_size: 200M # The directory on your host that store log location: /var/log/harbor # Uncomment following lines to enable external syslog endpoint. # external_endpoint: # # protocol used to transmit log to external endpoint, options is tcp or udp # protocol: tcp # # The host of external endpoint # host: localhost # # Port of external endpoint # port: 5140#This attribute is for migrator to detect the version of the .cfg file, DO NOT MODIFY!_version: 2.13.0# Uncomment external_database if using external database.# external_database:# harbor:# host: harbor_db_host# port: harbor_db_port# db_name: harbor_db_name# username: harbor_db_username# password: harbor_db_password# ssl_mode: disable# max_idle_conns: 2# max_open_conns: 0# Uncomment redis if need to customize redis db# redis:# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable# # registry_db_index: 1# # jobservice_db_index: 2# # trivy_db_index: 5# # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.# # harbor_db_index: 6# # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.# # cache_layer_db_index: 7# Uncomment external_redis if using external Redis server# external_redis:# # support redis, redis+sentinel# # host for redis: <host_redis>:<port_redis># # host for redis+sentinel:# # <host_sentinel1>:<port_sentinel1>,<host_sentinel2>:<port_sentinel2>,<host_sentinel3>:<port_sentinel3># host: redis:6379# password: # # Redis AUTH command was extended in Redis 6, it is possible to use it in the two-arguments AUTH <username> <password> form.# # there's a known issue when using external redis username ref:https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/issues/18892# # if you care about the image pull/push performance, please refer to this https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/wiki/Harbor-FAQs#external-redis-username-password-usage# # username:# # sentinel_master_set must be set to support redis+sentinel# #sentinel_master_set:# # tls configuration for redis connection# # only server-authentication is supported# # mtls for redis connection is not supported# # tls connection will be disable by default # tlsOptions:# enable: false# # if it is a self-signed ca, please set the ca path specifically.# rootCA:# # db_index 0 is for core, it's unchangeable# registry_db_index: 1# jobservice_db_index: 2# trivy_db_index: 5# idle_timeout_seconds: 30# # it's optional, the db for harbor business misc, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.# # harbor_db_index: 6# # it's optional, the db for harbor cache layer, by default is 0, uncomment it if you want to change it.# # cache_layer_db_index: 7# Uncomment uaa for trusting the certificate of uaa instance that is hosted via self-signed cert.# uaa:# ca_file: /path/to/ca# Global proxy# Config http proxy for components, e.g. http://my.proxy.com:3128# Components doesn't need to connect to each others via http proxy.# Remove component from `components` array if want disable proxy# for it. If you want use proxy for replication, MUST enable proxy# for core and jobservice, and set `http_proxy` and `https_proxy`.# Add domain to the `no_proxy` field, when you want disable proxy# for some special registry.proxy: http_proxy: https_proxy: no_proxy: components: - core - jobservice - trivy# metric:# enabled: false# port: 9090# path: /metrics# Trace related config# only can enable one trace provider(jaeger or otel) at the same time,# and when using jaeger as provider, can only enable it with agent mode or collector mode.# if using jaeger collector mode, uncomment endpoint and uncomment username, password if needed# if using jaeger agetn mode uncomment agent_host and agent_port# trace:# enabled: true# # set sample_rate to 1 if you wanna sampling 100% of trace data; set 0.5 if you wanna sampling 50% of trace data, and so forth# sample_rate: 1# # # namespace used to differentiate different harbor services# # namespace:# # # attributes is a key value dict contains user defined attributes used to initialize trace provider# # attributes:# # application: harbor# # # jaeger should be 1.26 or newer.# # jaeger:# # endpoint: http://hostname:14268/api/traces# # username:# # password:# # agent_host: hostname# # # export trace data by jaeger.thrift in compact mode# # agent_port: 6831# # otel:# # endpoint: hostname:4318# # url_path: /v1/traces# # compression: false# # insecure: true# # # timeout is in seconds# # timeout: 10# Enable purge _upload directoriesupload_purging: enabled: true # remove files in _upload directories which exist for a period of time, default is one week. age: 168h # the interval of the purge operations interval: 24h dryrun: false# Cache layer configurations# If this feature enabled, harbor will cache the resource# `project/project_metadata/repository/artifact/manifest` in the redis# which can especially help to improve the performance of high concurrent# manifest pulling.# NOTICE# If you are deploying Harbor in HA mode, make sure that all the harbor# instances have the same behaviour, all with caching enabled or disabled,# otherwise it can lead to potential data inconsistency.cache: # not enabled by default enabled: false # keep cache for one day by default expire_hours: 24# Harbor core configurations# Uncomment to enable the following harbor core related configuration items.# core:# # The provider for updating project quota(usage), there are 2 options, redis or db,# # by default is implemented by db but you can switch the updation via redis which# # can improve the performance of high concurrent pushing to the same project,# # and reduce the database connections spike and occupies.# # By redis will bring up some delay for quota usage updation for display, so only# # suggest switch provider to redis if you were ran into the db connections spike around# # the scenario of high concurrent pushing to same project, no improvement for other scenes.# quota_update_provider: redis # Or db# 复制cp harbor.yml.tmpl harbor.yml# 查看cat harbor.yml | grep -v '#' | grep -v '^$'说明:生成ssl证书见“3、配置Harbor的HTTPS访问(如果使用https访问,请配置)”
hostname: 【修改为ip或域名,192.168.186.128】http: port: 【修改端口,8080】https: port: 【修改端口,8443】 certificate: 【指定证书,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.crt】 private_key: 【指定密钥,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.key】 internal_tls: enabled: true dir: 【tls目录,/etc/harbor/tls/internal】harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345database: password: root123 max_idle_conns: 100 max_open_conns: 900 conn_max_lifetime: 5m conn_max_idle_time: 0data_volume: 【数据映射目录,/data】trivy: ignore_unfixed: false skip_update: false skip_java_db_update: false offline_scan: false security_check: vuln insecure: false timeout: 5m0sjobservice: max_job_workers: 10 max_job_duration_hours: 24 job_loggers: - STD_OUTPUT - FILEnotification: webhook_job_max_retry: 3log: level: info local: rotate_count: 50 rotate_size: 200M location: 【日志目录,/var/log/harbor】_version: 2.13.0proxy: http_proxy: https_proxy: no_proxy: components: - core - jobservice - trivyupload_purging: enabled: true age: 168h interval: 24h dryrun: falsecache: enabled: false expire_hours: 24
# ./install.sh --with-trivy./install.sh
# 命令:tree harbor# 内容:harbor|-- common| `-- config| |-- core| | |-- app.conf| | |-- certificates| | `-- env| |-- db| | `-- env| |-- jobservice| | |-- config.yml| | `-- env| |-- log| | |-- logrotate.conf| | `-- rsyslog_docker.conf| |-- nginx| | |-- conf.d| | `-- nginx.conf| |-- portal| | `-- nginx.conf| |-- registry| | |-- config.yml| | |-- passwd| | `-- root.crt| |-- registryctl| | |-- config.yml| | `-- env| `-- shared| `-- trust-certificates|-- common.sh|-- docker-compose.yml|-- harbor.yml|-- harbor.yml.tmpl|-- install.sh|-- LICENSE|-- prepare`-- ssl |-- ca.crt |-- ca.key |-- ca.srl |-- v3.ext |-- yourdomain.com.cert |-- yourdomain.com.crt |-- yourdomain.com.csr `-- yourdomain.com.key15 directories, 29 files# 查看运行的容器列表docker ps# ----------------------------# 创建并启动容器docker-compose up -d# 停止并销毁容器docker-compose down# ----------------------------# 启动容器docker start 容器ID/名称# 停止容器docker stop 容器ID/名称# 重启容器docker restart 容器ID/名称# 删除停止的容器docker rm 容器ID/名称wget https://github.com/goharbor/harbor/releases/download/v2.13.0/harbor-offline-installer-v2.13.0.tgz
tar -xf harbor-offline-installer-v2.13.0.tgz
harbor├── common.sh├── harbor.v2.13.0.tar.gz├── harbor.yml.tmpl├── install.sh├── LICENSE└── prepare0 directories, 6 filescd harbor
# 复制cp harbor.yml.tmpl harbor.yml# 查看cat harbor.yml | grep -v '#' | grep -v '^$'说明:生成ssl证书见“3、配置Harbor的HTTPS访问(如果使用https访问,请配置)”
hostname: 【修改为ip或域名:192.168.186.128】http: port: 【修改端口:8080】https: port: 【修改端口:8443】 certificate: 【指定证书,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.crt】 private_key: 【指定密钥,/data/cert/yourdomain.com.key】 internal_tls: enabled: true dir: 【tls目录,/etc/harbor/tls/internal】harbor_admin_password: Harbor12345database: password: root123 max_idle_conns: 100 max_open_conns: 900 conn_max_lifetime: 5m conn_max_idle_time: 0data_volume: 【数据映射目录,/data】trivy: ignore_unfixed: false skip_update: false skip_java_db_update: false offline_scan: false security_check: vuln insecure: false timeout: 5m0sjobservice: max_job_workers: 10 max_job_duration_hours: 24 job_loggers: - STD_OUTPUT - FILEnotification: webhook_job_max_retry: 3log: level: info local: rotate_count: 50 rotate_size: 200M location: 【日志目录,/var/log/harbor】_version: 2.13.0proxy: http_proxy: https_proxy: no_proxy: components: - core - jobservice - trivyupload_purging: enabled: true age: 168h interval: 24h dryrun: falsecache: enabled: false expire_hours: 24
# ./install.sh --with-trivy./install.sh
# 命令:tree harbor# 内容:harbor├── common│ └── config│ ├── core│ │ ├── app.conf│ │ ├── certificates│ │ └── env│ ├── db│ │ └── env│ ├── jobservice│ │ ├── config.yml│ │ └── env│ ├── log│ │ ├── logrotate.conf│ │ └── rsyslog_docker.conf│ ├── nginx│ │ ├── conf.d│ │ └── nginx.conf│ ├── portal│ │ └── nginx.conf│ ├── registry│ │ ├── config.yml│ │ ├── passwd│ │ └── root.crt│ ├── registryctl│ │ ├── config.yml│ │ └── env│ └── shared│ └── trust-certificates├── common.sh├── docker-compose.yml├── harbor.v2.13.0.tar.gz├── harbor.yml├── harbor.yml.tmpl├── install.sh├── LICENSE├── prepare└── ssl ├── ca.crt ├── ca.key ├── ca.srl ├── v3.ext ├── yourdomain.com.cert ├── yourdomain.com.crt ├── yourdomain.com.csr └── yourdomain.com.key15 directories, 30 files# 查看运行的容器列表docker ps# ----------------------------# 创建并启动容器docker-compose up -d# 停止并销毁容器docker-compose down# ----------------------------# 启动容器docker start 容器ID/名称# 停止容器docker stop 容器ID/名称# 重启容器docker restart 容器ID/名称# 删除停止的容器docker rm 容器ID/名称假设当前ip为192.168.186.128浏览器访问:http://192.168.186.128:8080 或者 https://192.168.186.128:8443默认管理员账户密码均为:admin Harbor12345
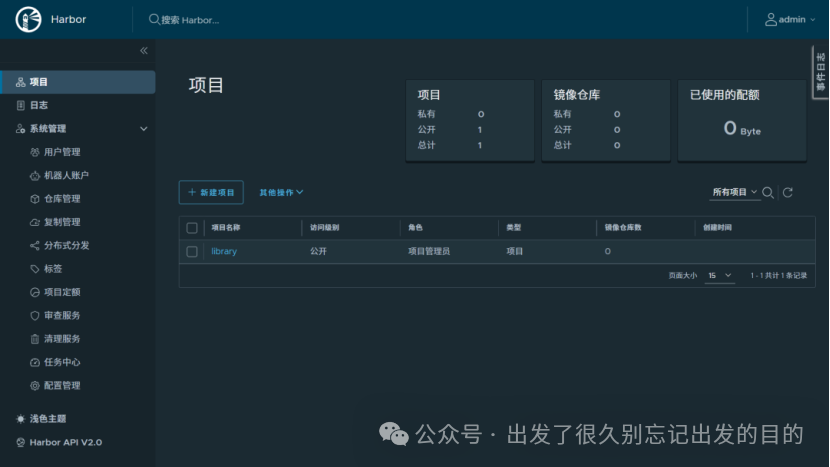
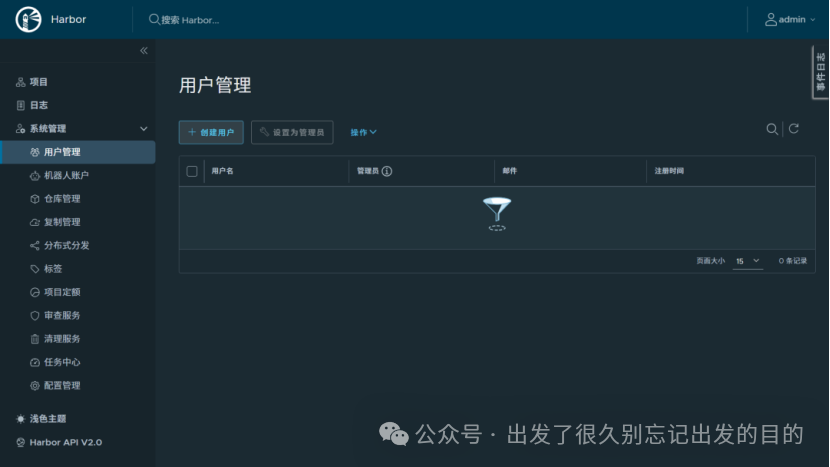
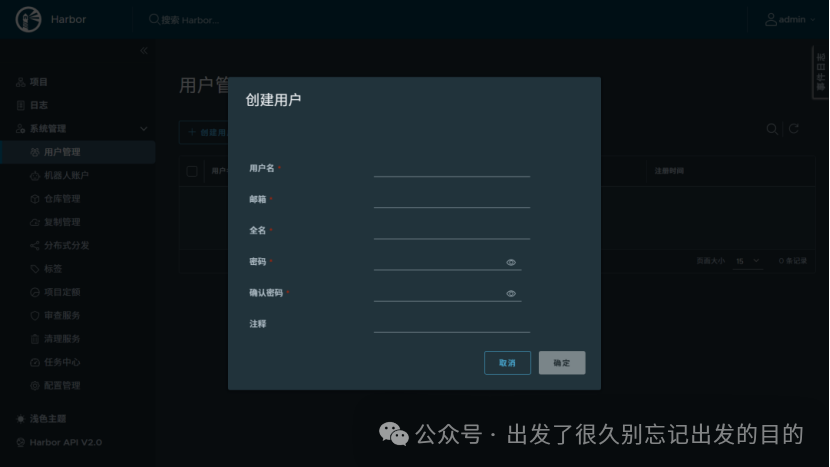
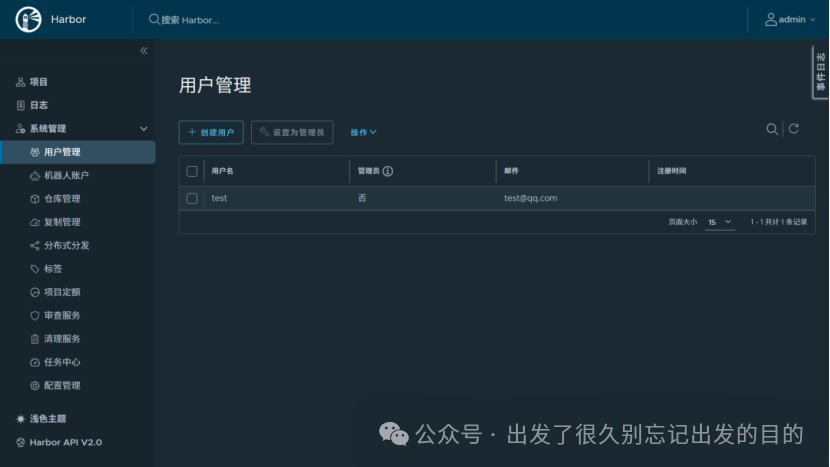
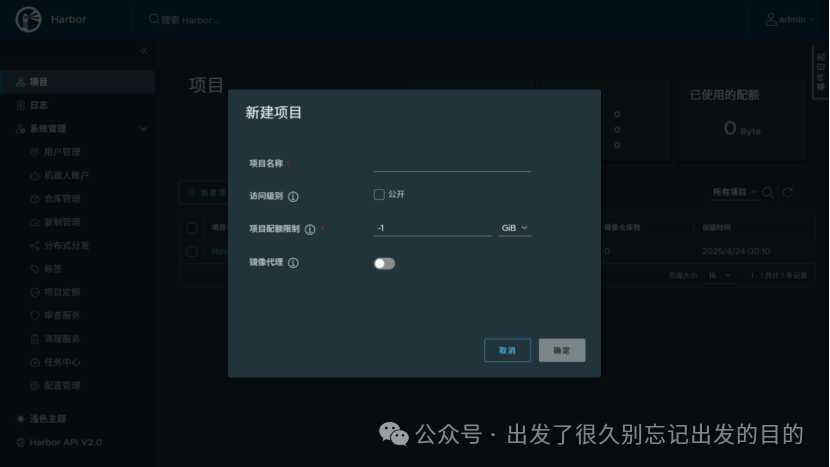
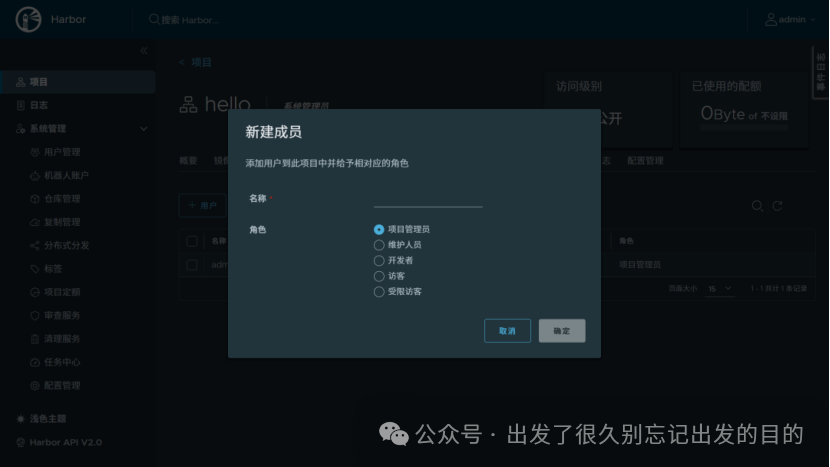
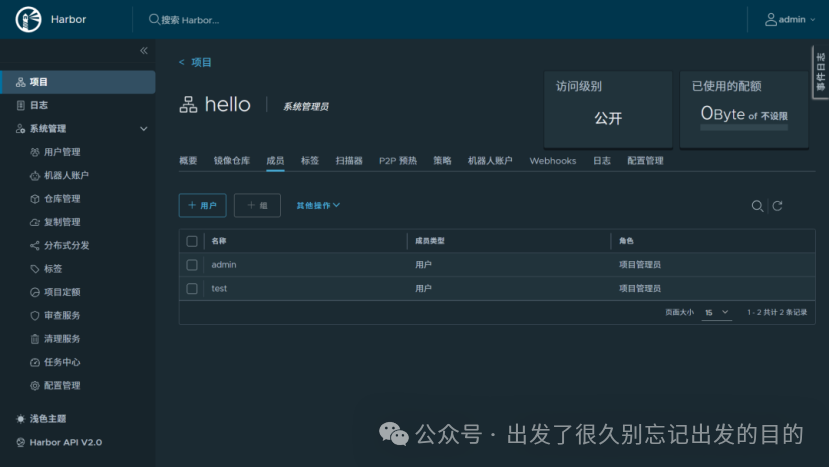
# https://docs.docker.com/reference/dockerfile/FROM alpine:latestWORKDIR /rootRUN echo hello > halo.txt
docker build -t 192.168.186.128:8080/hello/halo:v1 .# docker build -t 192.168.186.128:8443/hello/halo:v1 .# 登录docker login 192.168.186.128:8080# docker login 192.168.186.128:8443# 退出docker logout 192.168.186.128:8080# docker logout 192.168.186.128:8443docker push 192.168.186.128:8080/hello/halo:v1# docker push 192.168.186.128:8443/hello/halo:v1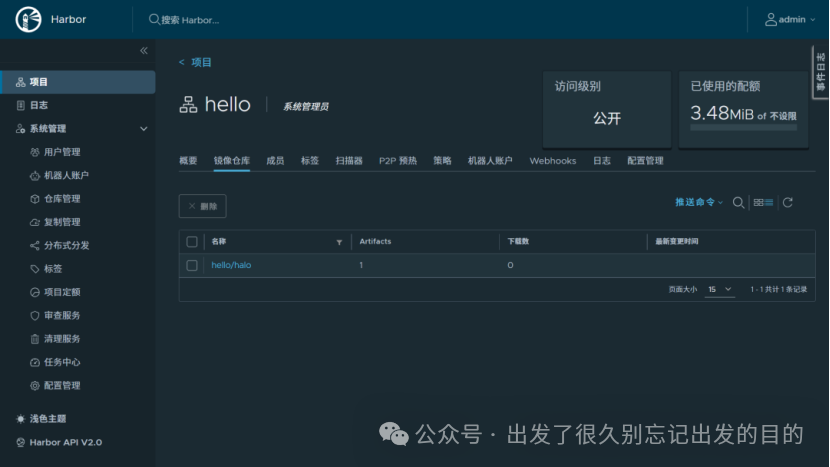
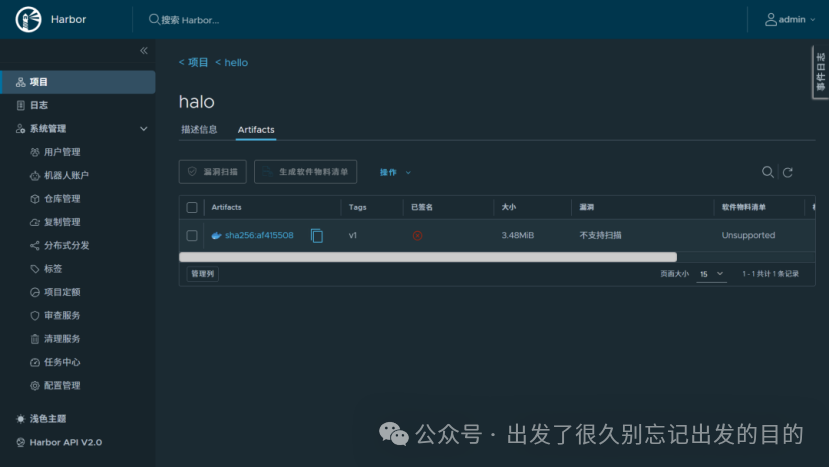
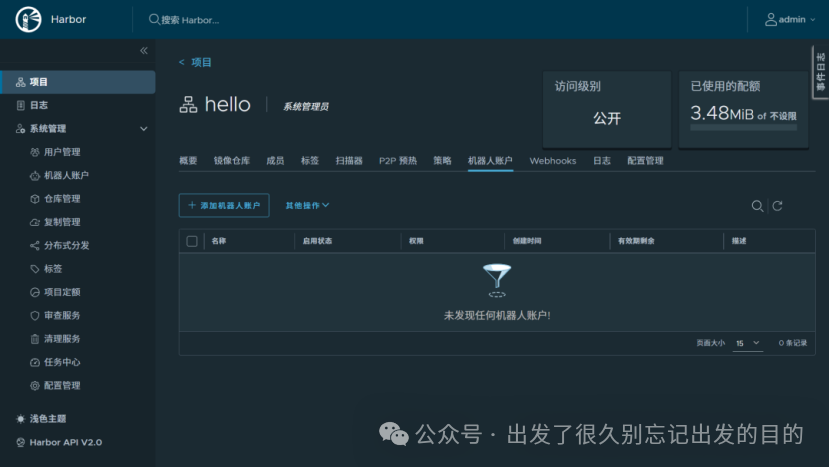
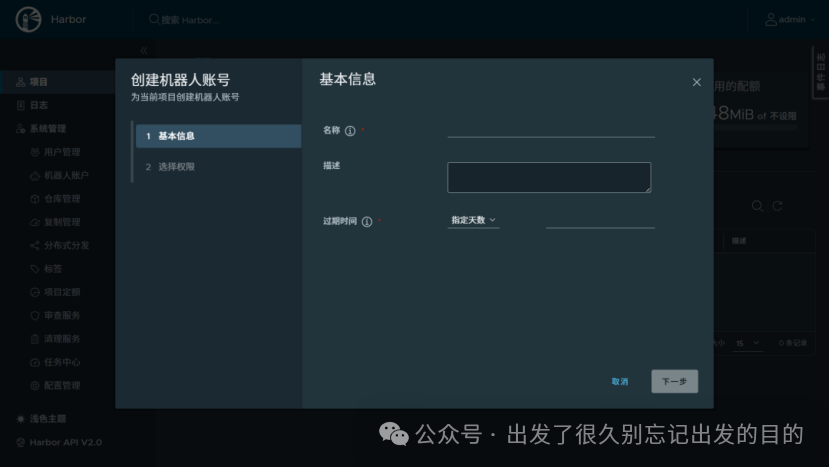
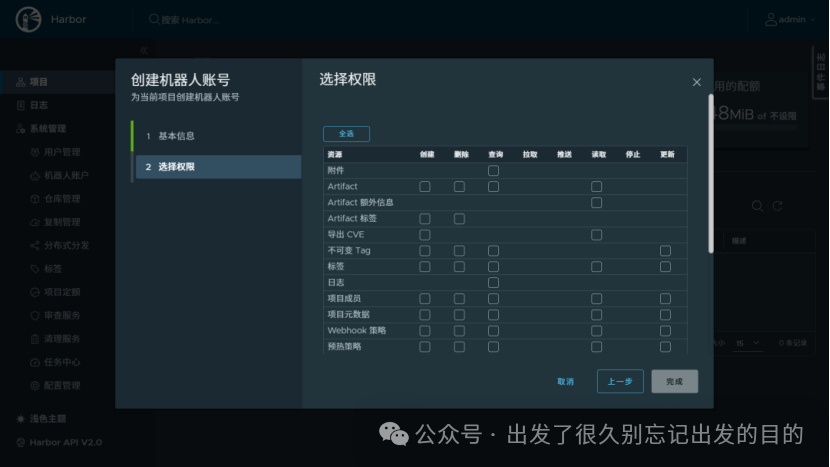
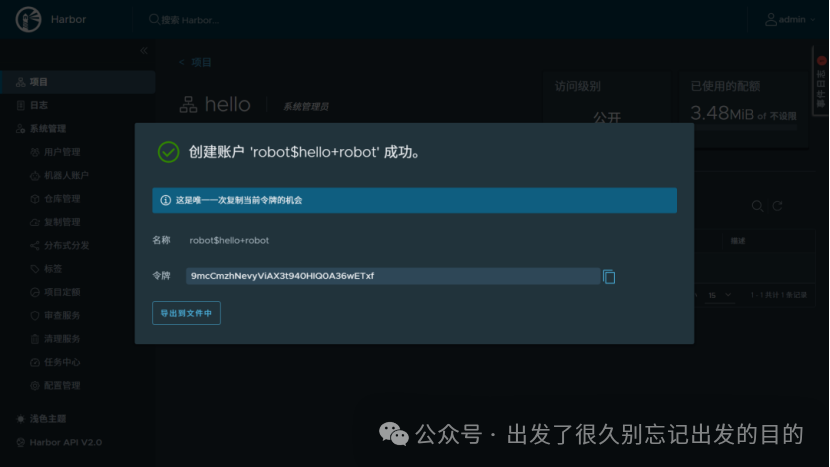
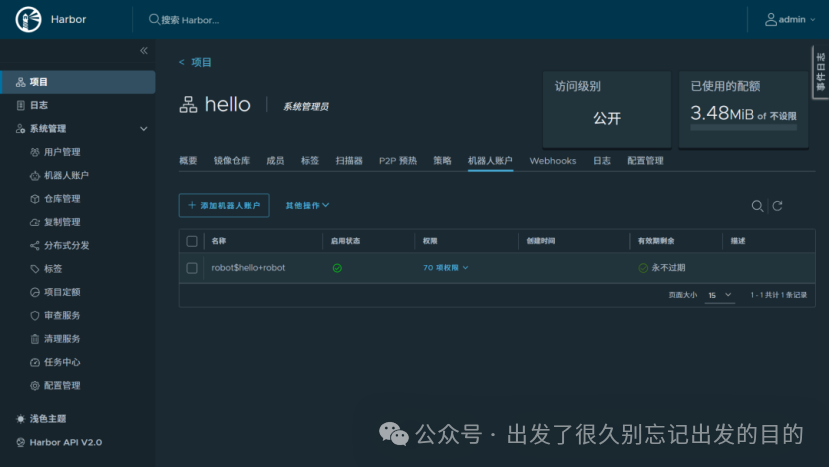
# 文件名:robot$hello+hello.json# 文件内容:{"creation_time":"yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.000Z","expires_at":-1,"id":3,"name":"robot$hello+robot","secret":"9mcCmzhNevyViAX3t940HIQ0A36wETxf"}# 参数说明:# creation_time:创建时间# expires_at:过期时间# id:用户ID# name:机器人账户# secret:令牌/密码# https://docs.docker.com/reference/dockerfile/FROM alpine:latestWORKDIR /root
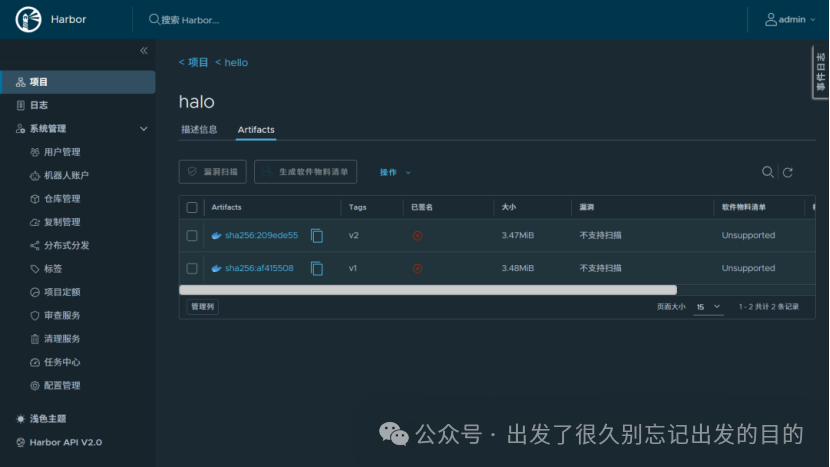
docker build -t 192.168.186.128:8080/hello/halo:v2 .# docker build -t 192.168.186.128:8443/hello/halo:v2 .# 用户名:robot$hello+robot# 密码:9mcCmzhNevyViAX3t940HIQ0A36wETxf# 登录docker login 192.168.186.128:8080# docker login 192.168.186.128:8443# 退出docker logout 192.168.186.128:8080# docker logout 192.168.186.128:8443docker push 192.168.186.128:8080/hello/halo:v2# docker push 192.168.186.128:8443/hello/halo:v2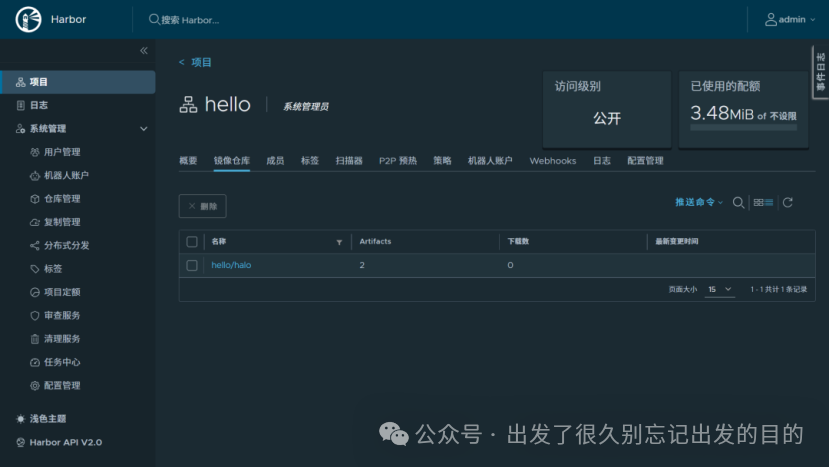
https://goharbor.io/
本文链接:https://www.kinber.cn/post/6146.html 转载需授权!
推荐本站淘宝优惠价购买喜欢的宝贝:

 支付宝微信扫一扫,打赏作者吧~
支付宝微信扫一扫,打赏作者吧~